Slow Pyrolysis
Slow pyrolysis differs from fast pyrolysis in that: it provides longer residence times, sometimes on the order of greater the 5 seconds, or even minutes or days; low reactions temperatures, less than 400 °C; atmospheric pressure operation; low heating rates, from 0.01 to 2 °C per second; and low thermal quenching of products, because of the low reaction temperature. Char is formed proportionately to the mass of reacting material because of intraparticle gas phase reactions, however a lower carbon footprint is said to be produced using this method.
Flow Diagrams
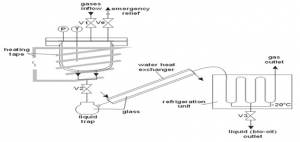
(Source: http://www.carbolea.ul.ie/area.php?=pyrolysis)
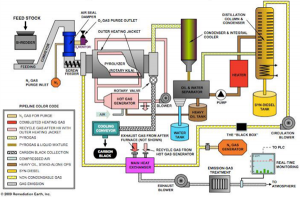
(Source: http://www.greservices.com/index.php/community/blog-opinion/1-web-blog/83-slow-pyrolysis-explained)
Equipment
Videos
References
- http://www.ewb.org.au/explore/initiatives/openchar/techproduction/slowpyrolysis
- http://www.biocharnow.com/biochar/slow-pyrolysis
- http://www.carbolea.ul.ie/area.php?=pyrolysis
- http://www.greservices.com/index.php/community/blog-opinion/1-web-blog/83-slow-pyrolysis-explained